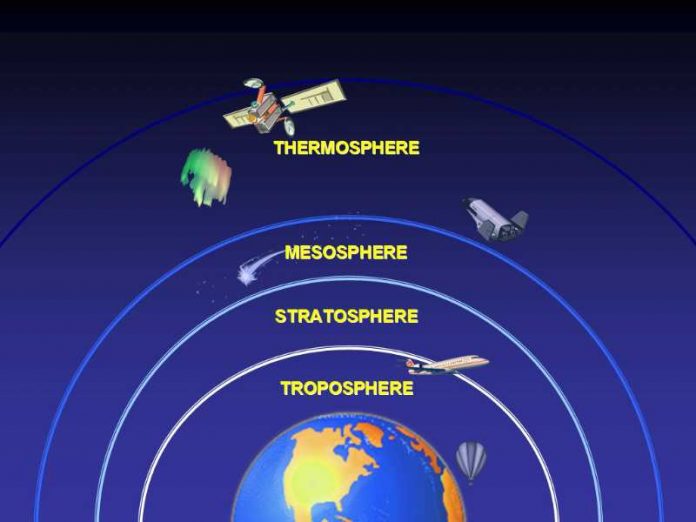
EARTH’S ATMOSPHERE LAYERS
- EXOSPHERE
- THERMOSPHERE OR IONOSPHERE (I)
- MESOSPHERE (M)
- STRATOSPHERE (S)
- TROPOSPHERE (T)
To learn the sequence(remember this sentence):
I am(M) (S)Sachin (T)Tendulkar.
EXOSPHERE (5th layer):
- This is the upper limit of our atmosphere.
- It extends from the top of the thermosphere up to 10,000 km (6,200 mi).
- There is no clear upper boundary of this layer.
THERMOSPHERE OR IONOSPHERE (4th layer):
- It extends from about 90 km (56 miles) to between 500 and 1,000 km.
- The space shuttle and the International Space Station both orbit Earth within the thermosphere.
- Energetic ultraviolet and X-ray photons from the Sun also break apart molecules in the thermosphere. In the upper thermosphere, atomic oxygen (O), atomic nitrogen (N), and helium (He) are the main components of air.
- IONOSPHERE -> It allows radio waves to travel across the country to another city.
MESOSPHERE (3rd layer):
- The mesosphere starts just above the stratosphere and extends to 85 kilometers (53 miles) high.
- Meteors burn up in this layer.
- Weather balloons and other aircraft cannot fly high enough to reach the mesosphere.
STRATOSPHERE (2nd layer):
-
The stratosphere starts just above the troposphere and extends to 50 kilome(31miles) high.
-
The ozone layer, which absorbs and scatters the solar ultraviolet radiation, is in this layer.
- Jet aircraft and weather balloons reach their maximum operational altitudes within the stratosphere because air is very thin here.
TROPOSPHERE (1st layer):
- The troposphere starts at the Earth’s surface and extends 8 to 14.5 kilometers high (5 to 9 miles).
- In this layer we live in.
- The bottom of the troposphere is at Earth’s surface.
- This part of the atmosphere is the most dense.
- Most types of clouds are found in this layer.
- Almost all weather is in this region.